Double Entry
Double Entry accounting is a core feature of Focal Suite's financial management system, designed to record transactions by making entries in two distinct accounts: debit and credit. Each transaction impacts both sides of the accounting equation, ensuring that assets always equal liabilities plus equity. This approach helps businesses maintain precise financial records, monitor their financial well-being, and stay compliant with accounting standards, all within the seamless framework of Focal Suite.
Dual Accounting Principle
Maintain Balance And Accuracy in Accounting
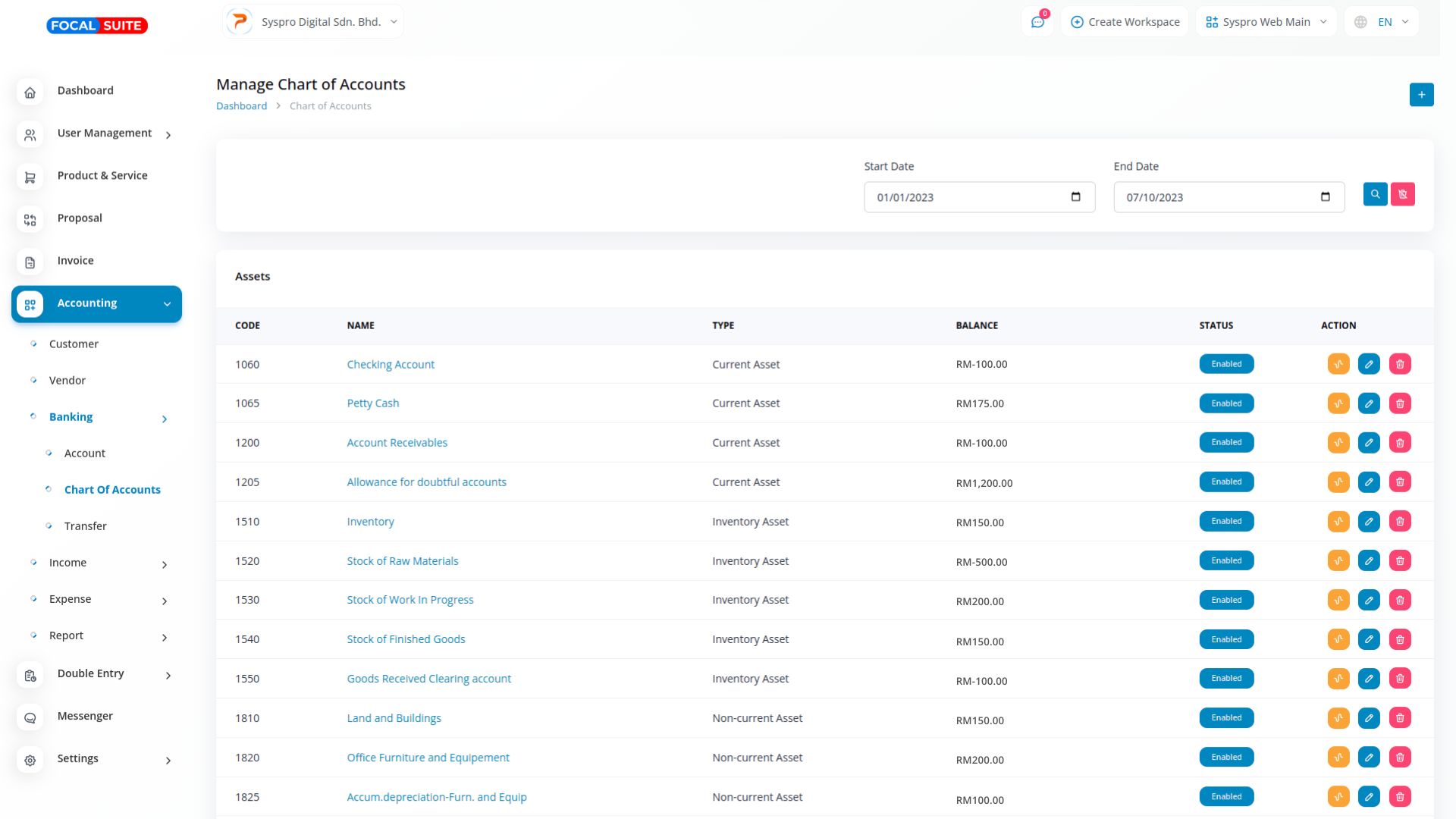
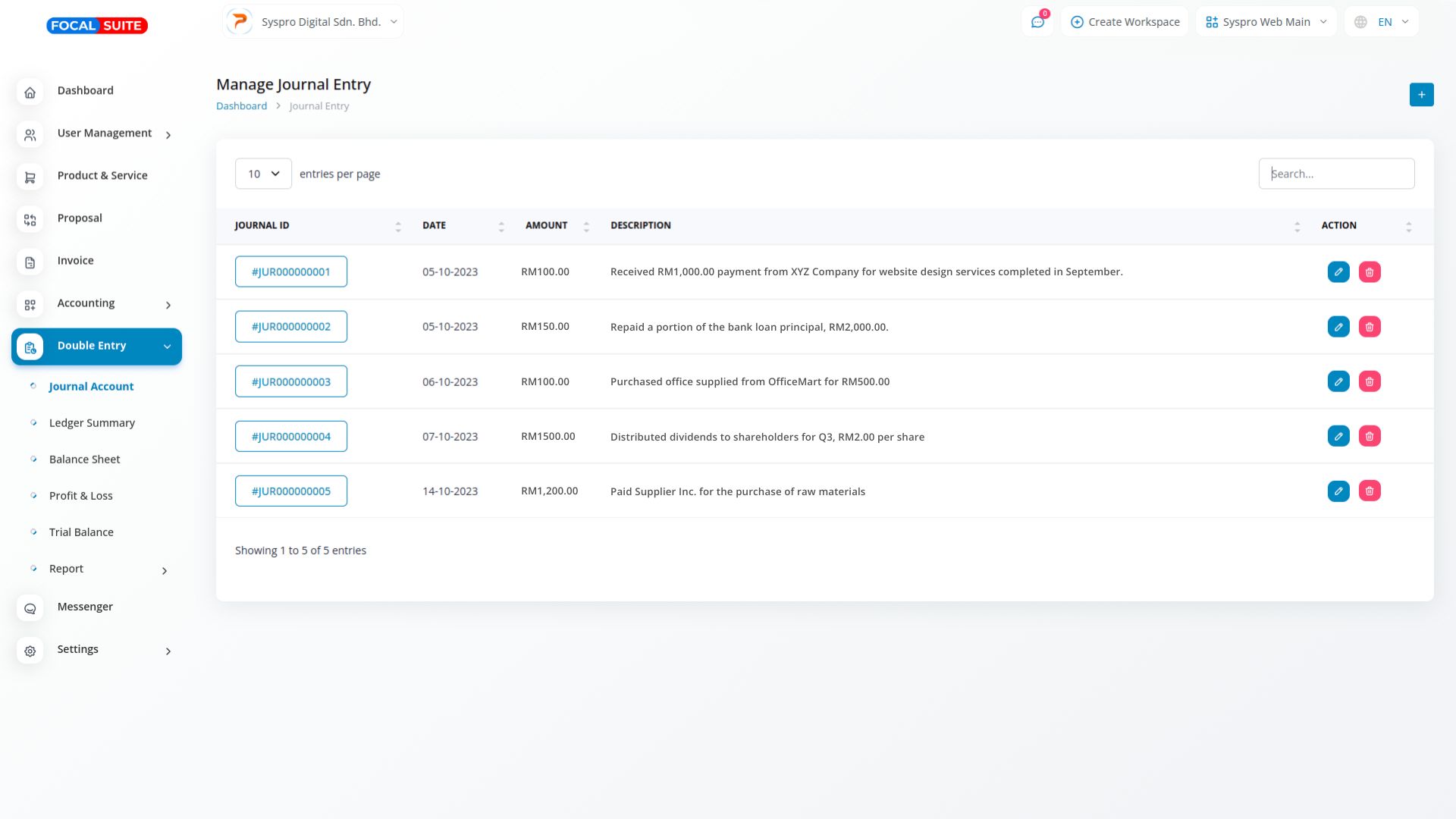
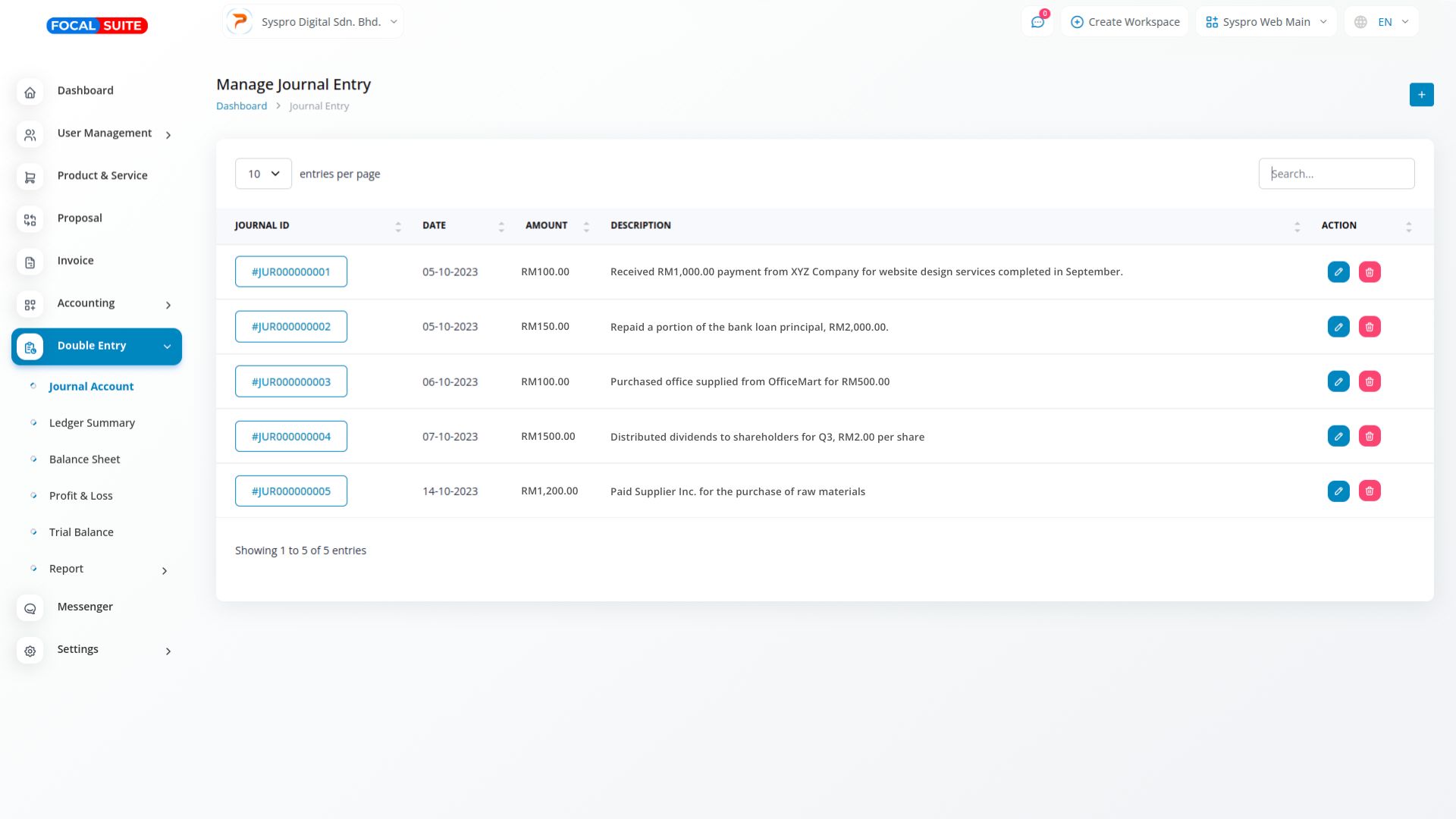
A Journal Account is a key component of the double entry accounting system, used to record individual financial transactions. Each transaction is entered with both a debit and a credit in the journal account, ensuring that the accounting equation (assets = liabilities + equity) stays balanced and accurate. This process helps maintain the integrity of a company’s financial records.
To perform accounting journal entries, first identify the transaction and analyze its effect on relevant accounts. Then, record the transaction in a journal by assigning appropriate debit and credit entries. Ensure the entries balance, and finally, post them to the general ledger to maintain accurate financial reporting.
Tools for keeping an accurate general ledger
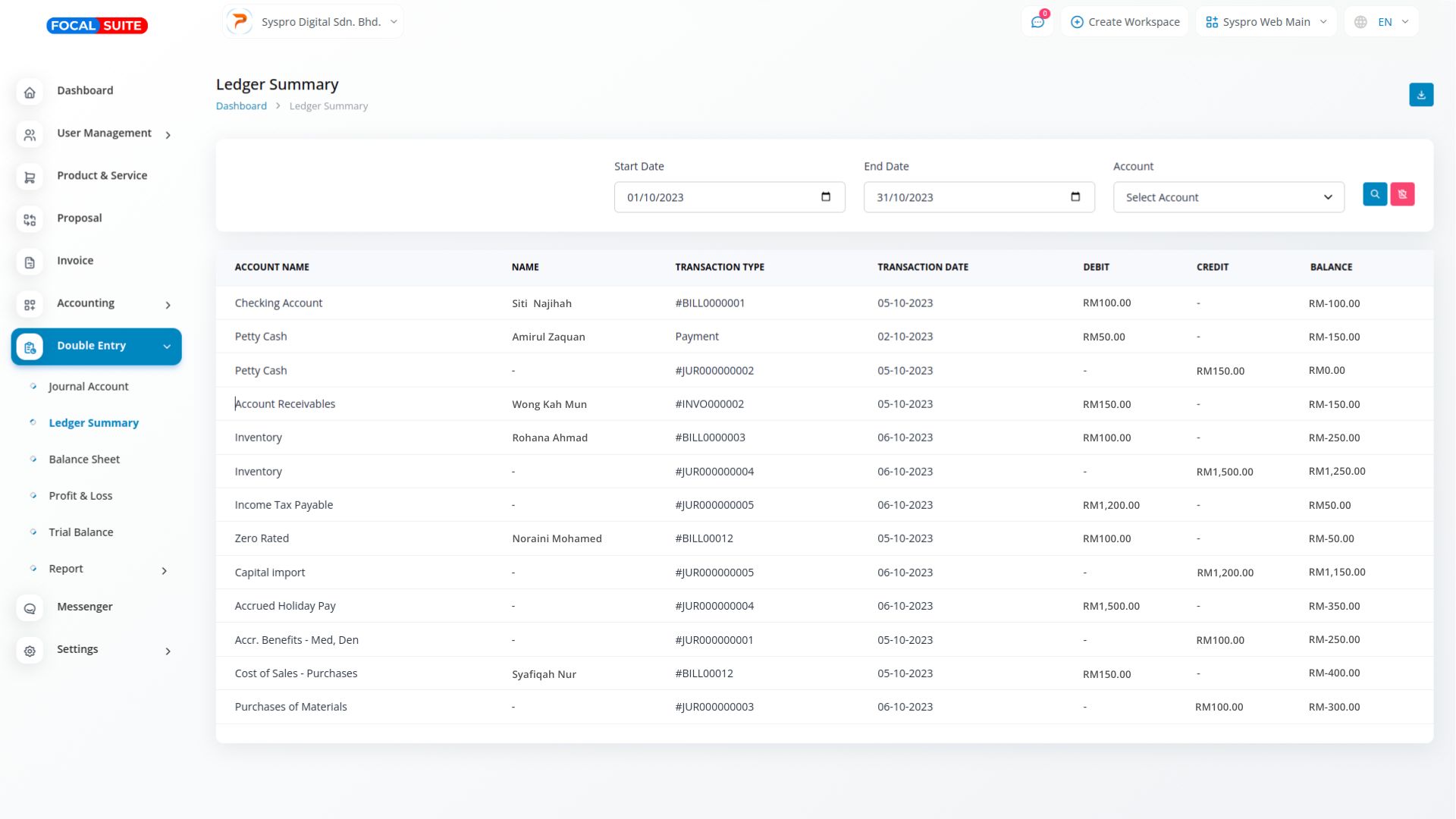
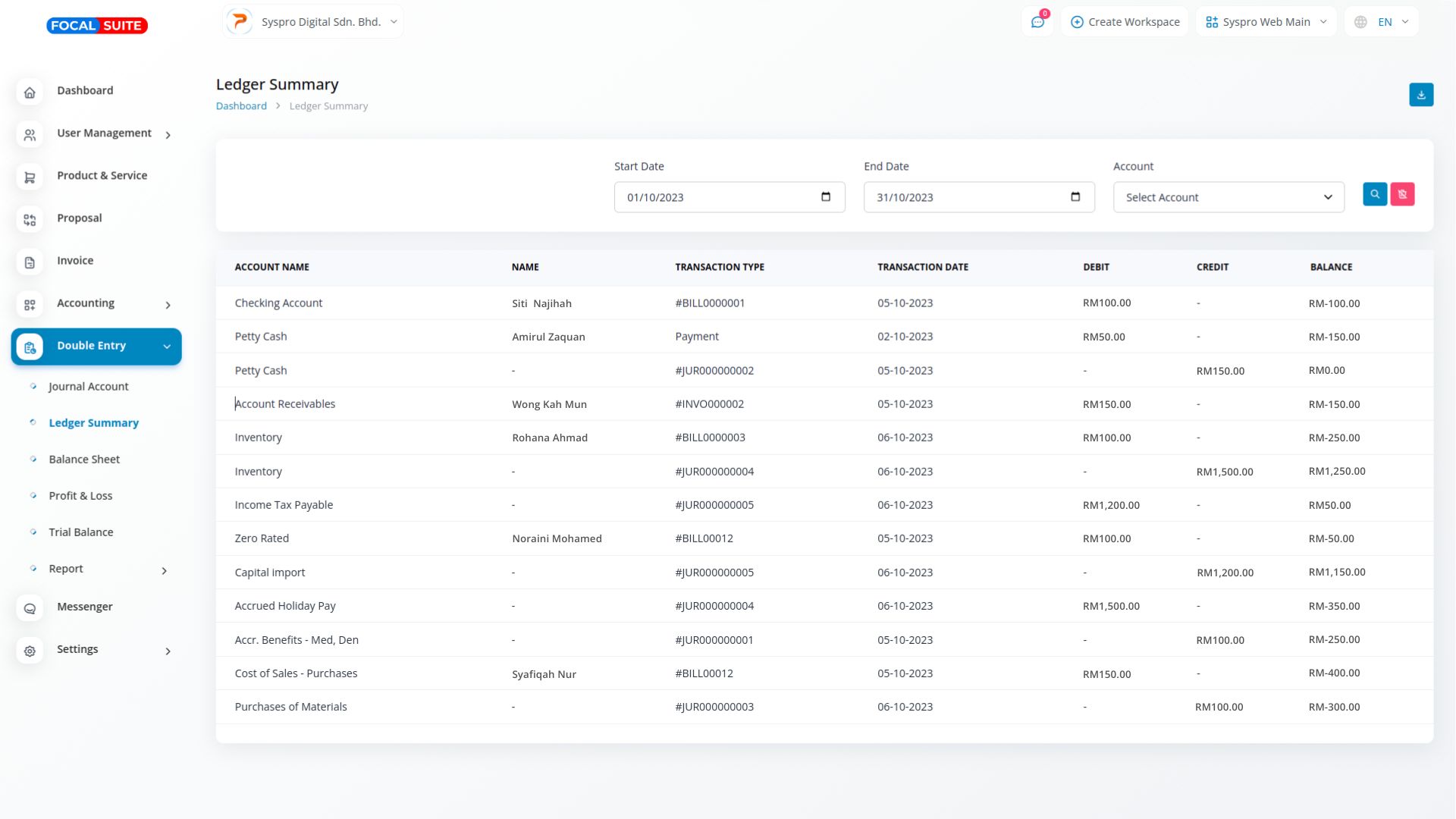
A ledger account is a detailed record of all transactions impacting a specific account within the general ledger. Each transaction is documented with a date, transaction number, and description, providing business owners and accountants with clear information to easily trace and understand the purpose behind each transaction.
A ledger account keeps a record of all transactions related to a specific account, helping businesses monitor financial activity. Each entry shows debits, credits, and balances, making it easier to track the financial history of individual accounts and ensure accuracy in financial management.
Ledger accounts include detailed information like dates, transaction numbers, and descriptions. This allows business owners and accountants to quickly identify and research the reasons behind specific transactions, promoting transparency and supporting informed decision-making in financial analysis.
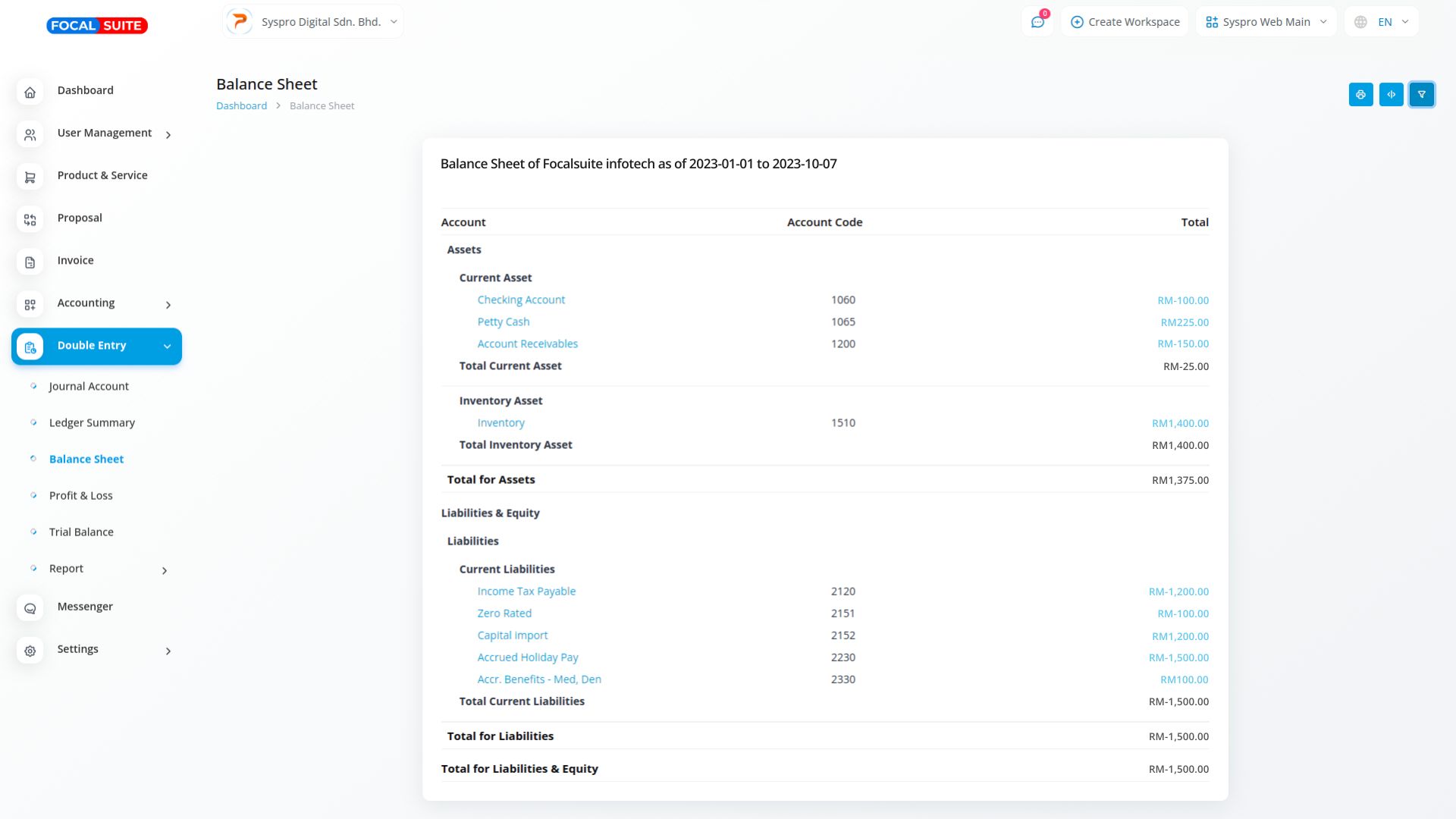
Balance Sheet
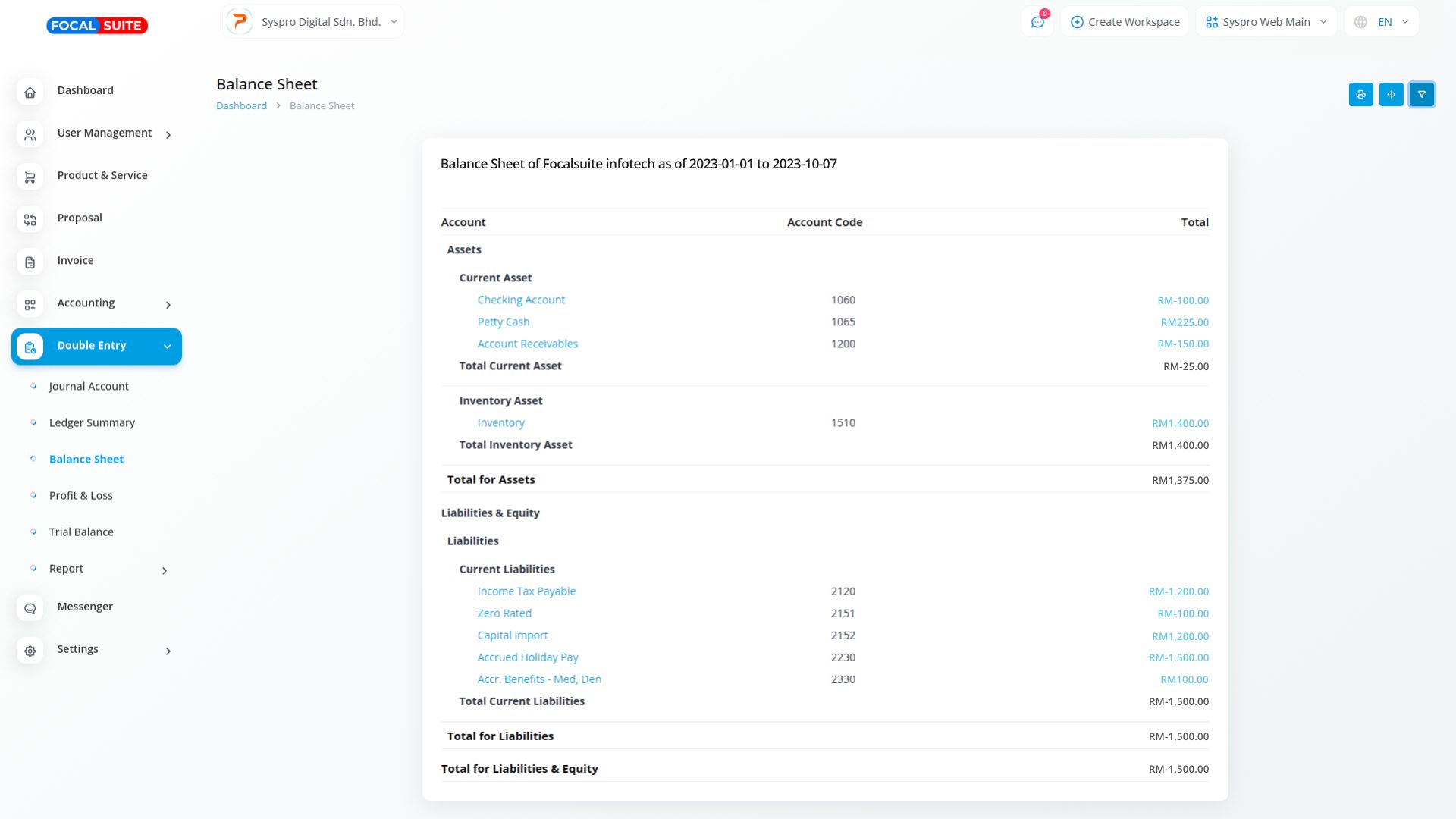
Balance sheets offer a clear snapshot of a company's financial position by detailing its assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific moment. Assets represent what the company owns, liabilities indicate what it owes, and equity reflects ownership. The core equation, Assets = Liabilities + Equity, ensures that assets always match the total of liabilities and equity, maintaining financial balance.
A balance sheet provides a quick overview of a company's financial health by showing the relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity. This enables stakeholders to assess a company's stability, liquidity, and financial performance at a specific point in time.
The balance sheet relies on the equation Assets = Liabilities + Equity, ensuring that all financial data is correctly balanced. This equation reflects the company's financial structure and helps verify that assets are funded through either debt (liabilities) or ownership (equity).
Profit and Loss (P&L) Statement
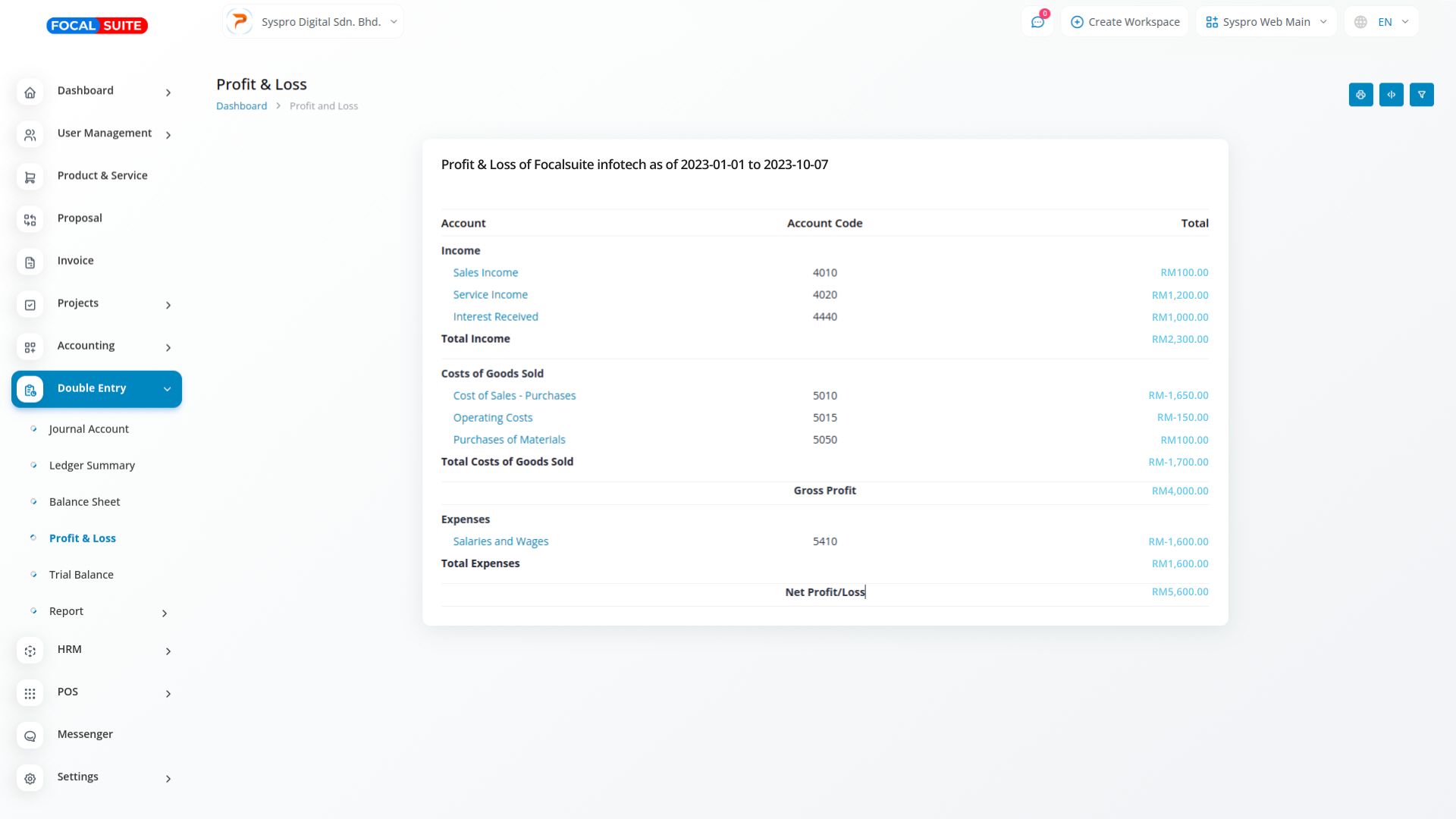
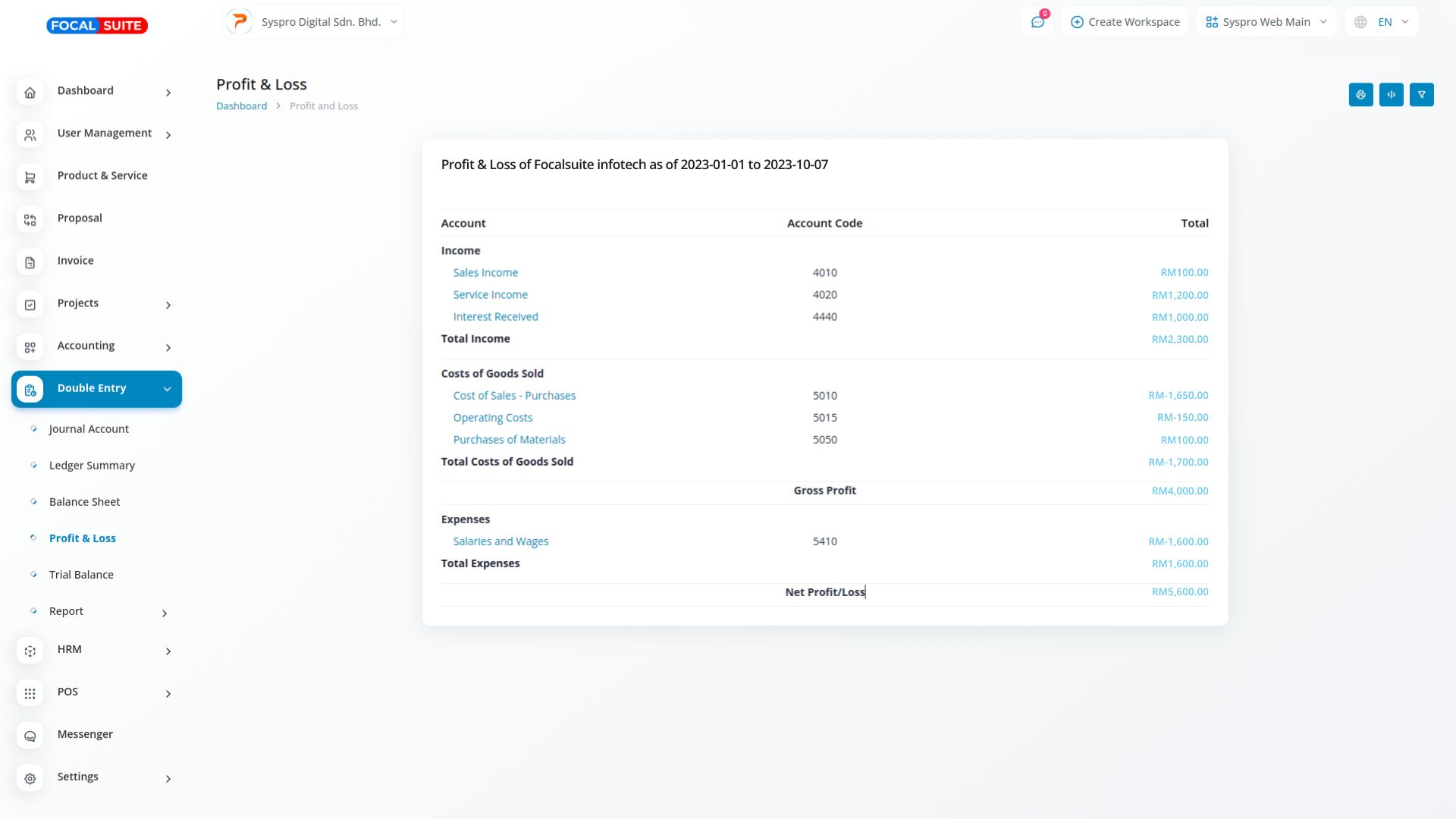
Profit and Loss (P&L) statements, or income statements, offer a comprehensive financial overview of a company’s performance over a defined period. Beginning with total revenues from sales, they deduct operating expenses such as cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, taxes, and interest. The final net profit (or loss) reflects the company’s bottom-line earnings after all expenses are accounted for.
P&L statements detail both revenue and expenses, allowing businesses to monitor their financial performance. By breaking down different types of income and costs, these statements help identify trends and areas for improvement, enabling better strategic decision-making.
By comparing P&L statements across different periods, companies can assess their profitability and operational efficiency. This analysis helps stakeholders understand how well the business is performing, identify potential financial issues, and make informed projections for future growth.
Trial Balance
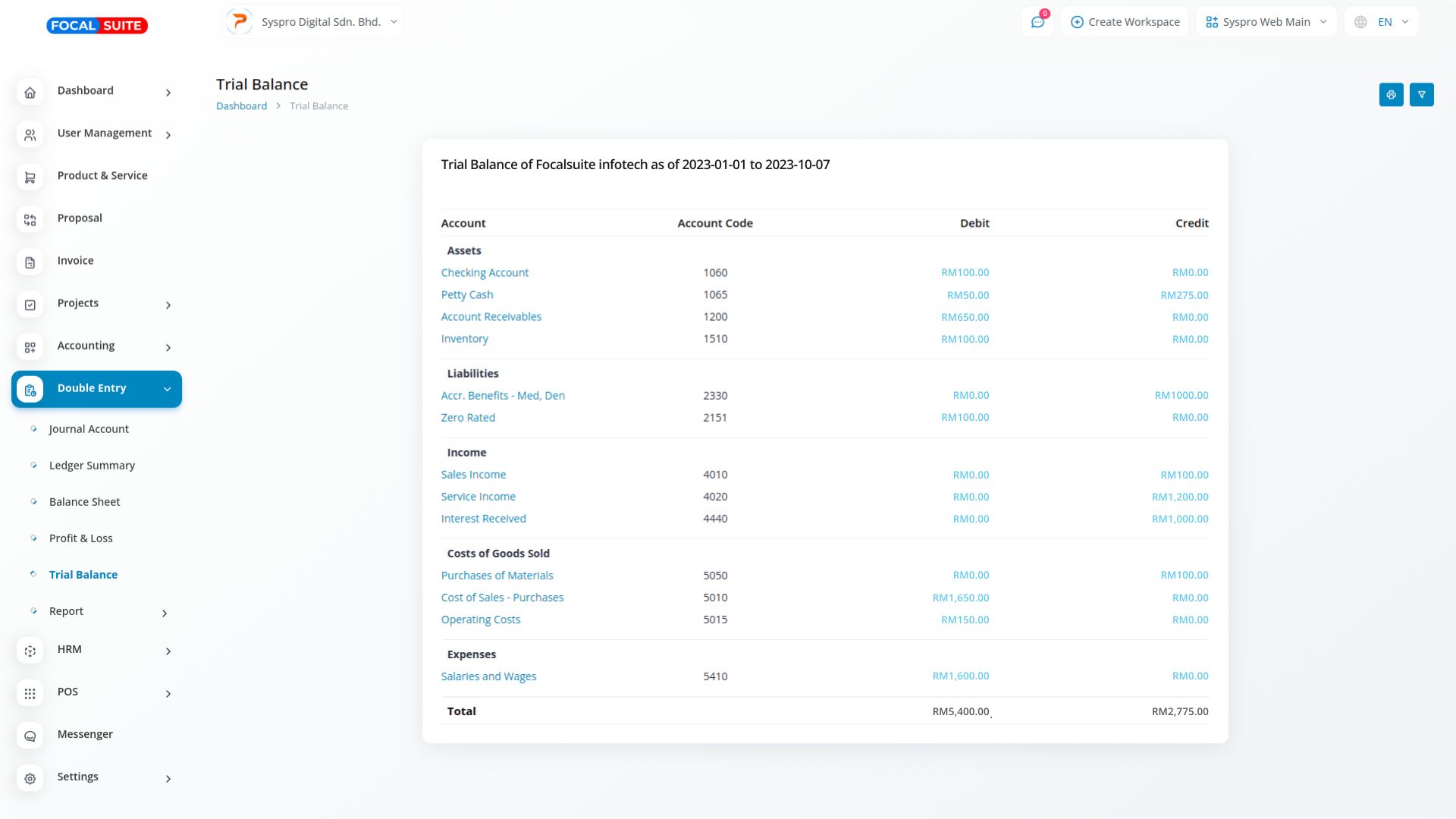
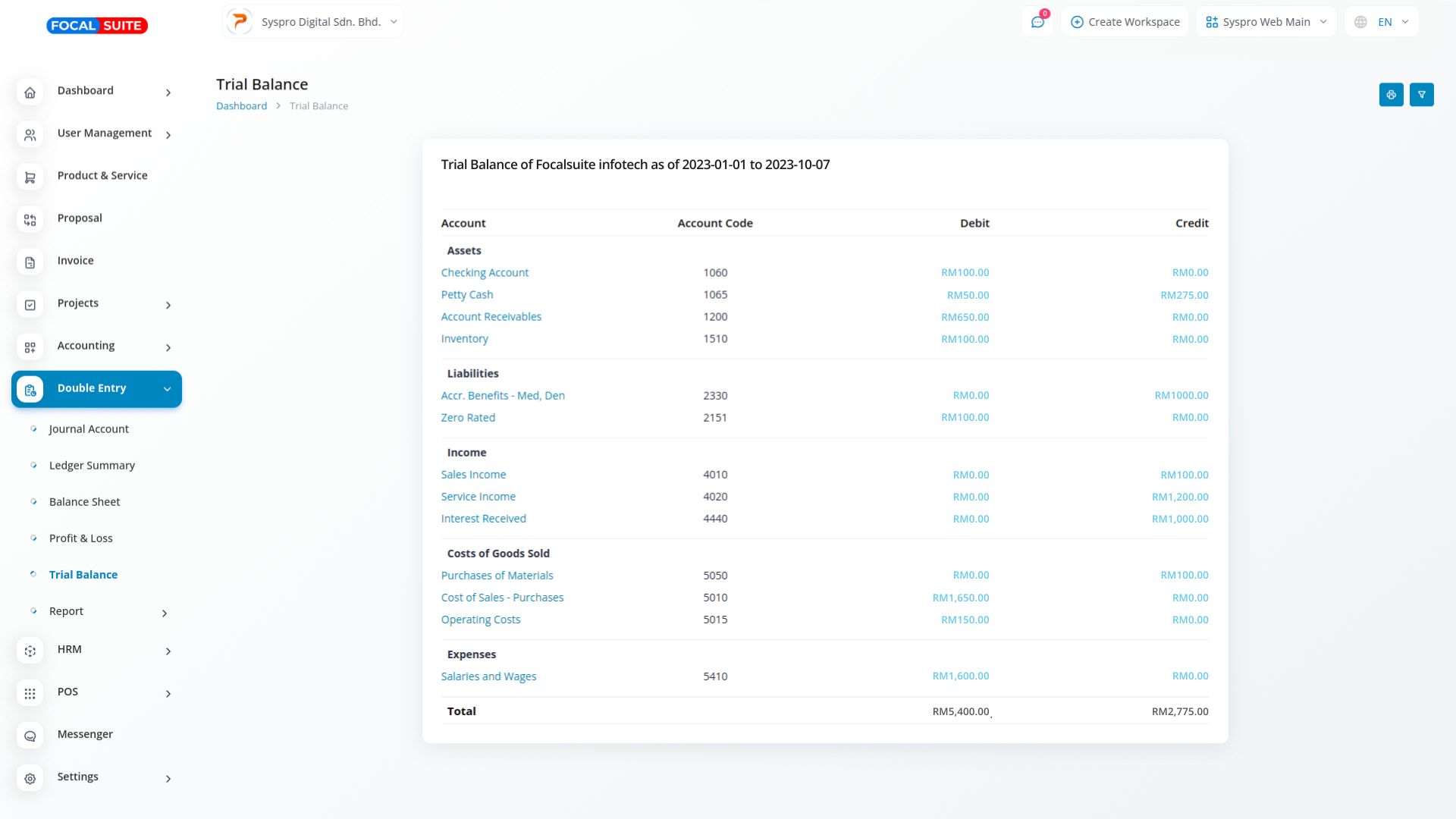
A Trial Balance is an essential accounting worksheet that compiles all general ledger accounts along with their respective balances. It acts as a crucial verification tool, ensuring that total debits equal total credits. This balance confirms the accuracy of financial data across key accounting categories, including assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, expenses, gains, and losses.
The Trial Balance serves as a preliminary check to ensure that all financial transactions are recorded accurately. By confirming that total debits equal total credits, it helps identify errors in the accounting records before financial statements are prepared, ensuring reliability in financial reporting.
A well-prepared Trial Balance simplifies the process of generating financial statements by providing a summary of all account balances. This organized overview aids accountants in efficiently drafting the balance sheet and income statement, ensuring all components align correctly for comprehensive financial analysis.
Why choose dedicated addon for Your Business?
Empower Your Workforce with Focal Suite
Access over Premium Add-ons for Accounting, HR, Payments, Leads, Communication, Management, and more, all in one place!
- Pay-as-you-go
- Unlimited installation
- Secure cloud storage
Why choose dedicated addon for Your Business?
With Focal Suite, you can conveniently manage all your business functions from a single location.